What is financial modeling and common models to know
Predicting the future is a daunting task, unless you possess a time machine like Marty McFly in the 1985 film, 'Back to the Future'. If you don’t have such a tool, the next best thing is financial modeling. It can offer valuable insights and guidance into the future financial position of your business.
What is financial modeling?
Financial modeling is the process of building a summary of a company’s income and expenses to better predict it’s future finances. A financial model usually takes the form of a spreadsheet, though it doesn’t always have to.
Financial modeling relies on historical data from finance and operations to formulate and predict future insights. These insights are used for accurate financial forecasting and projecting your resilience for the year ahead as well as risks areas. A financial model is the narrative of your company's journey and where it's headed. This blueprint is more than data in an Excel spreadsheet – crunched for your needs; it must tell the story and strategy of your business in a language everyone can understand. It paints a connected picture of your financial standing, capturing the past, present, and future trajectory of your business.
In essence, a financial model translates your business plan into numbers, offering a detailed breakdown of revenue, expenses, and growth prospects. When built in a business planning and analytics platform, you can quickly test different scenarios and anticipate outcomes, enabling you to make informed decisions and rally your team and stakeholders around a unified vision that have been consulted about and agreed on.
At Phocas, our customers like the fact that we have robust data integrations that connects seamlessly with their ERP and inventory systems, ensuring that their financial models are based on accurate data.
Financial models serve various financial planning purposes, but in this blog we will concentrate on how they help mostly with budgeting and forecasting. We discuss why this financial planning and analysis (fp&a) practice is necessary for CFOs and leaders to predict future financial performance effectively.
Common Uses for Financial Models
Financial models serve various financial planning purposes within mid-market business so whether you are planning for the next 5-years or looking for an injection of funds, financial models are paramount.
Budgeting and forecasting
Financial models serve as a basis for budgeting and forecasting activities. They help businesses set realistic financial targets, allocate resources effectively, and monitor progress toward achieving financial goals. Within the budget, finance teams can also do scenario planing and make informed choices about investments, expansion, pricing strategies, and resource allocation. Financial modeling in budgets helps businesses forecast future financial performance, which is crucial for strategic planning and decision-making.
Contingency planning
Businesses can assess and manage risks by identifying potential pitfalls and developing contingency plans with financial models. By simulating different scenarios, companies can anticipate and mitigate financial risks such as changes in interest or tax rates, inflation or unexpected expenses.
KPI tracking
Once the financial model in your budget is set it serves as a vital benchmark for evaluating actual financial performance and financial KPIs like the growth rate once the books are closed each month. When you have automatic dataflow that inputs into your budget and financial statements, comparing actuals with budget and identifying variances of metrics is immediate.
Being able to gain insights into the underlying causes of the variances and then take appropriate corrective action helps avoid surprises and is good upkeep of your model.
Better collaboration
Financial models provide a common framework for communication and collaboration between different stakeholders such as sales, operations, human resources, finance, investors, lenders, and board members. They help convey complex financial information in a structured and understandable format, facilitating discussions and alignment of interests and business decisions. It also serves as an accountability tool, keeping everyone on track and aligned with the company's objectives.
Common types of financial modeling
There are several types of financial models, each serving a specific purpose and offering unique advantages. In this analysis, we will explore seven distinct types of financial models starting with the most essential to more specific models.
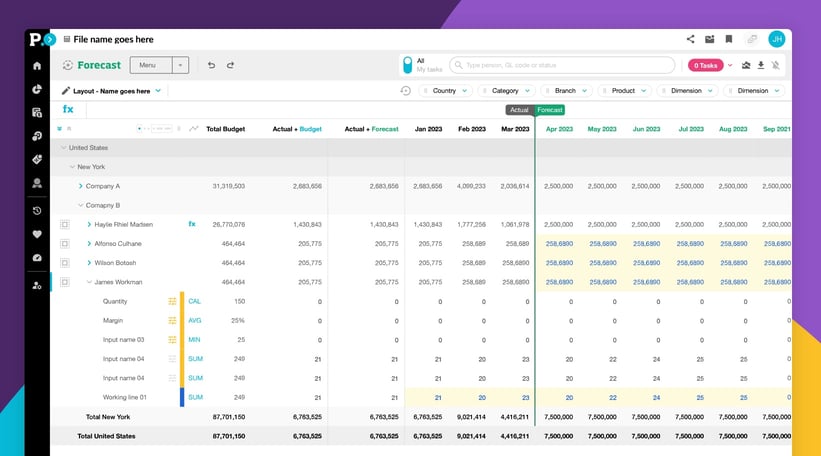
We consider these four financial models: the budget model, the 3-statement model, the consolidation model, and the forecasting model to be integral to the day-to-day operation of a business and they are readily available in the Phocas business planning and analytics platform. These models give business owners and CFOs the ability to effectively align strategy with budget, manage cash flow, balance the books across all business divisions, and adapt the budget to address evolving market conditions in line items and customer preferences.
Budget Model
The budget model is a financial plan that forecasts revenue growth, expenses, and cash flows over a specific period, typically one to five years. It allocates resources to achieve organizational objectives. It’s the master plan that connects your strategy and all of its specific tactics with your financial resources. It is also important to monitor actual performance against budgeted targets, and identifying variances for reforecasts. The budget model enables effective financial planning, resource allocation, and performance management. It provides a roadmap for achieving organizational goals and when using a platform like Phocas to create a model there are various templates that can be ued. These have been created with accountants and are designed to help drive collaboration and with automatic data access, comparing actuals with budget numbers and reforecasting is quickly achievable each month.
Three statement model
The three-statement model is a comprehensive FP&A tool that integrates the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. It offers a holistic view of a company's financial data and performance, specifically relating to cash flow over a specific period.
This model serves multiple purposes, including financial analysis, sensitivity analysis valuation, and strategic planning. It enables the evaluation of a company's profitability, liquidity, and solvency, while also facilitating the forecasting of future financial performance.
The three statement model provides valuable insights into a company's financial performance, aids in strategic decision-making, and serves as a foundation for more advanced financial modeling techniques.
Consolidation Model
The consolidation model combines the financial statements of multiple entities into a single set of financial statements, typically for a parent company and its subsidiaries.
Frequently utilized for companies who have multiple enities and for mergers and acquistions. It helps in presenting a unified view of the financial performance and position of a group of companies. It ensures accurate financial reporting and compliance with regulatory requirements.
The purpose of preparing consolidated financial statements is to provide an in-depth view of the financial performance and financial position of a group of companies as if they were a single entity.
This serves a dual function: offering insights into the collective performance of the group and enhancing transparency for stakeholders. When companies operate under a parent company-subsidiary relationship, stakeholders, including investors and regulatory bodies, seek a consolidated view to assess the overall health and stability of the group. In Phocas Financial Statements, consolidated models are achievable and each statement can be made into clear visualizations.
Forecasting model
A forecasting financial model is often used to manage operations in-house and when the budget model and financial statements are linked it is realtively easy to reforecast each month. The model has a lot of detail around their operations information and it rolls forward each month to add another forecast. It uses information from the three financial statements.
Its primary purpose is to provide insights into potential revenue growth, expenses, and cash flow analysis, aiding in strategic decision-making and planning.
Financial models for startup and investors
Startups and established companies seeking to secure capital from investors or lenders will require information from specific financial modeling. Before committing funds, investors expect to review projections of future cash flows, profitability, and returns on investment. Creating compelling and well-grounded financial models plays a crucial role in attracting potential investors and securing funding.
Forecasting Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Model
The Forecasting Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) model is a valuation technique used to estimate the intrinsic value of an investment by discounting its projected future cash flows to present value. Discounting future cash flows involves determining the amount of money that needs to be invested presently, at a specific return rate, to generate the projected cash flow at a future date. In simpler terms, discounting calculates the present value of future cash flows, using a suitable cost of capital that accurately considers the risk and timing of the cash flows.
It is widely used in investment analysis for corporate finance and mergers and acquisitions. It helps assess the attractiveness of investment opportunities, determine fair market value for businesses, and make informed capital allocation decisions. Knowing how to build and interpret discounted cash flow models (DCF) is critical for investors, financial analysts, and corporate finance professionals. The DCF model provides a systematic approach to valuing investments, facilitates decision-making regarding capital expenditures and acquisitions, and enables investors to make informed investment decisions based on expected returns.
Sum of the Parts Model
The sum of the parts model involves valuing a company by valuing its business segments or divisions separately and then aggregating their values to determine the overall company's worth. It is particularly relevant for conglomerates with diverse business units or companies considering divestitures or spin-offs. Understanding the sum of the parts is valuable for investors, analysts, and corporate executives as it provides insights into the relative contribution of each business segment to the overall company's value. It helps in optimizing portfolio allocation, identifying opportunities for value creation, and maximizing shareholder value.
Option Pricing Model
Option pricing models are mathematical models used to calculate the theoretical value of options contracts, such as call and put options, based on various factors including underlying asset price, volatility, time to expiration, and interest rates. It is commonly used in financial markets for pricing options contracts, assessing risk, and hedging strategies. They are also employed in corporate finance for valuing employee stock options and derivative securities. Understanding option pricing models is essential for traders, investors, and financial professionals involved in options trading, risk management, and investment analysis. It provides insights into the fair value of options contracts, helps in formulating trading strategies, and mitigates risks associated with options positions.
Phocas helps with day-to-day financial modeling
While you may not possess a time machine akin to Marty McFly's, the Phocas business planning and analytics platform is made for mid-market business that want to enhance financial modelling by being able to include all the key elements for success such as comprehensive data, expertise of business partners and key drivers. Phocas makes financial modelling accessible. It’s straightforward to implement, easy to use, and can help boost business performance.
With Phocas, you can forecast and re-forecast in minutes, because the software is an analytics platform built to handle large datasets and run scenarios. Businesses can embrace the future with confidence, knowing that their decisions are grounded in data-driven, forward-looking insights.
In case you were curious about the real-world financial performance and income statement of the film Back to the Future - it was a financial success. It earned $381.1 million to become the highest-grossing film of 1985 worldwide.

Katrina is a professional writer with a decade of experience in business and tech. She explains how data can work for business people and finance teams without all the tech jargon.

How technology is fixing the finance talent shortage and bringing a renaissance
Accounting is one of the oldest professions, with double-entry bookkeeping tracing back to Roman merchants in the 14th century. And the genius of a system in which every transaction is recorded with an opposite entry in a different account continues to be standard practice. Just as accounting emerged during the shift from the Middle Ages to the Renaissance, today’s finance teams must also adapt to new challenges and opportunities.
Read more
5 key FP&A trends for 2025
The role of the CFO is evolving rapidly, extending beyond traditional financial stewardship to encompass business partnering, operational oversight and technological innovation. A 2024 Sage study of over 1,200 global finance leaders reinforces this transformation:
Read more
An accurate view of your business’ finances: it’s not too hard to get
Finance teams are increasingly under pressure to provide CEOs and other executives with information related to their business’ current financial scenario — but it’s not always easy for them to do so.
Read more
Demand planning and forecasting
For finance teams in manufacturing, distribution or retail, effective demand planning is critical to meeting customer expectations without tying up cash in excess inventory. When done right, it ensures the right products are available at the right time and in the right quantities.
Read more
Find out how our platform gives you the visibility you need to get more done.
Get your demo today