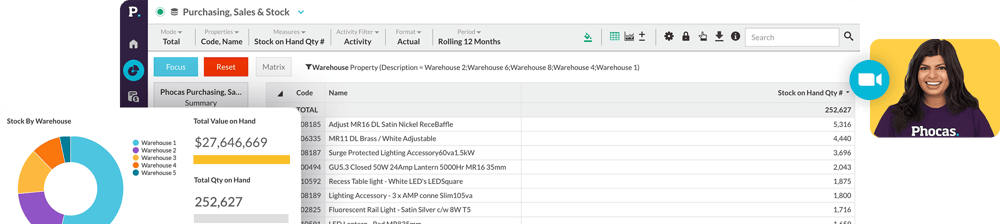
What is a data cube?
A data cube is a powerful way to organize and analyze large amounts of multidimensional data. Think of it as a structured, digital representation of information, designed to help businesses answer key performance questions quickly and efficiently. For industries like manufacturing, wholesale distribution, and retail, data cubes are essential tools that simplify data analysis, making it easier for cross-functional teams to identify trends, solve problems, and make decisions based on accurate information.
The structure of a data cube.
For example, in a retail context, a data cube might track sales figures across the dimensions of time (daily, weekly, monthly), store locations, and product categories. The multidimensional data structure enables users to focus on specific data subsets, like sales performance in a particular region during a holiday season.
Key features and operations
Data cubes are designed to make complex data analysis fast and user-friendly. Several data cube operations are used to extract valuable insights:
- Slicing isolates a single dimension, such as analyzing sales data for a specific product.
- Dicing creates a more detailed view by narrowing down multiple dimensions, like examining sales of a product in one region over the last quarter.
- Drill-down explores finer-grained details within a dimension, such as moving from monthly sales to daily figures.
- Pivoting changes the orientation of the data, providing a new way to view relationships or trends.
- Roll-up aggregates data to a higher level, such as total yearly revenue instead of monthly totals.
These operations enable scalability, helping businesses to work with their data efficiently and accurately despite its increased complexity; large datasets from multiple data sources, including relational databases, spreadsheets, and data warehouses.
Why data cubes matter in BI and FP&A
How Phocas makes data cubes easy to use
1. Auto data consolidation
Phocas pulls data from multiple data sources, including ERP systems, Microsoft tools, and other systems, into one centralized platform or data model. This ensures that the information is always up-to-date and accessible for all users. For example, a company in manufacturing can use Phocas to integrate production schedules, inventory levels, and sales forecasts into a single, cohesive cube.
2. Dynamic dashboards and visualization
With Phocas, you don’t just analyze data—you can see it come to life. The software uses intuitive visualization tools and dashboards to present aggregate data in a way that’s easy to understand at a glance. Finance teams can quickly identify trends, such as revenue spikes during specific periods, and adjust their strategies accordingly.
3. Real-time insights and advanced features
Phocas’ data cubes support real-time updates and advanced capabilities like machine learning algorithms to enhance forecasting and planning. Teams can create time-series analyses to understand changes over time or leverage cached results for fast performance during high-demand queries.
4. User-Friendly Semantics
Phocas emphasizes making data cubes accessible for users of all levels. Through thoughtful design, the platform simplifies hierarchies, semantics, and operations like drill-down and pivoting, so even non-technical users can gain insights without needing SQL expertise.
Phocas data cube use case examples
- Retail sales analysis: A retail manager using Phocas can drill into sales data from multiple stores, compare product category performance, and analyze seasonal trends—all within the same cube. This capability eliminates the need for disconnected spreadsheets or manual calculations.
- Manufacturing forecasting: For a manufacturer, a data cube can model production costs against inventory levels, sales forecasts, and supply chain timelines. By rolling up data to view overall trends or drilling down to analyze costs by individual products, decision-makers can improve accuracy in budgeting and resource allocation.
Why use Phocas data cubes
Understand the past, operate better today, and plan well for the future