What is a balanced scorecard?
The balanced scorecard (BSC) is a powerful management tool designed to help organizations align their day-to-day activities with overarching strategic goals. Developed by Robert Kaplan and David P. Norton and popularized in the 1990s through the Harvard Business Review, the balanced scorecard approach revolutionized strategic management by providing a framework to measure and improve organizational performance. It offers a comprehensive view of performance beyond just financial measures, incorporating non-financial metrics like customer satisfaction and internal business processes.
The balanced scorecard Framework
The balanced scorecard organizes performance into four key perspectives:
- Financial perspective: Focuses on financial performance, return on investment (ROI), and profitability. It measures how effectively the organization delivers value to shareholders and stakeholders.
- Customer perspective: Highlights customer satisfaction, loyalty, and market share, reflecting how well the organization meets customer needs.
- Internal business processes: Examines internal processes critical to delivering high-quality products or services efficiently.
- Learning and growth perspective: Emphasizes employee development, innovation, and the infrastructure needed to support continuous improvement and future success.
These perspectives allow organizations to create a balanced view of their strategic performance, ensuring that short-term objectives do not undermine long-term sustainability.
Strategy Map and Strategic Planning
A strategy map is a visual representation of an organization’s strategy. It illustrates how strategic objectives in each perspective connect to achieve the organization’s goals. By linking objectives such as financial results, customer satisfaction, and new product development, strategy maps support effective decision-making and strategy execution.
Incorporating the balanced scorecard into strategic planning ensures that all levels of the organization work toward shared goals. It also helps prioritize initiatives and allocate resources efficiently, driving overall business performance.
Performance Measures and Metrics
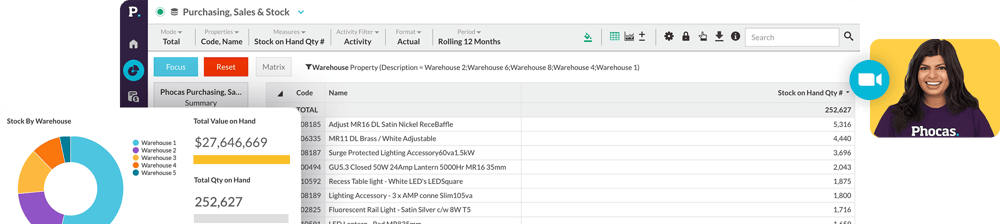
The BSC relies on clearly defined performance measures or key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress. Metrics are chosen to align with the organization’s unique business strategy and may include measures like financial perspective metrics (revenue growth), internal processes metrics (cycle times in manufacturing), and learning and growth indicators (employee training hours). Platforms like Phocas BI and FPA can help business people measure all financial and operational metrics by integrating all ERP data and other sources. The automation in Phocas enhances data collection, reporting, and analysis, enabling organizations to focus on continuous improvement rather than manual tasks. Creating a balanced scorecard can also be streamlined using pre-designed templates.
Benefits of the balanced scorecard approach
The balanced scorecard helps translate strategy into action becoming a cornerstone of performance management.
It offers a methodology to:
- Drive performance across all business units
- Achieve a competitive advantage by aligning the organization’s strategy with execution
- Improve stakeholder engagement by communicating progress effectively
With its focus on integrating financial results and non-financial metrics, the balanced scorecard continues to be a leading framework for improving organizational performance and enabling strategy execution in today’s complex environments.
Understand the past, operate better today, and plan well for the future