What is aggregate data?
Aggregate data refers to the process of compiling and summarizing raw data from different sources into a unified form for data analysis. Instead of examining individual data points, aggregate data provides a high-level overview of trends, anomalies and insights. This method is essential for making informed decisions in fields like manufacturing, distribution and retail.
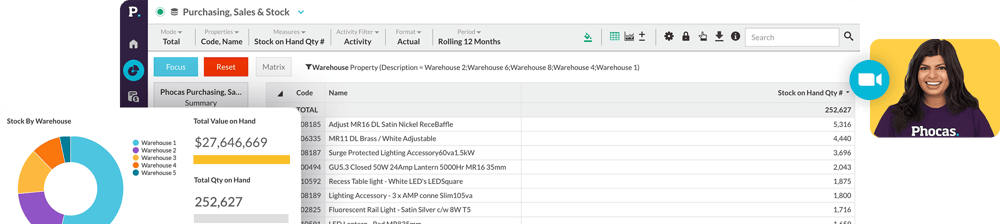
Aggregate data is the foundation of modern data analytics like the Phocas BI and FP&A platform, helping users to access insights from large datasets. By using SQL and advanced data aggregation tools, business people can drill into their data for better operational efficiency and to understand performance across sales, products and people.
Aggregate data vs raw data
Raw data is unprocessed information collected from data sources like spreadsheets, ecommerce systems, stock information, social media and customer surveys. It is granular and often contains personal or individual data – for example: a list of daily sales transactions for a store.
Aggregate data is a summarized form of raw data, often presented as summary statistics (averages, totals) or visualizations like dashboards – for example: daily sales summarized as a chart of weekly sales revenue.
How is aggregate data created?
The data aggregation process involves the following steps:
1. Data Collection Gather data from various sources, such as apps, ERPs, spreadsheets, SQL databases, or data warehouses.
2. Data Management Organize and store the collected data. This step often includes cleaning and formatting raw data to ensure consistency.
3. Aggregation and Processing Use data aggregation tools and algorithms to summarize information, such as grouping demographic information, calculating KPIs, or combining marketing metrics from multiple campaigns. This all happens automatically in the backend of Phocas so people can click buttons in the grid or use natural language processing to find an insight.
4. Visualization Display aggregated data on dashboards or other visualization tools for easy interpretation by data analysts, data scientists, and business leaders.
Use cases for aggregate data
1. Manufacturing Combine actual production hours per department and determine whether certain departments are under or over hours
2. Distribution Summarize sales data from different products and find bundles and opportunities for upsell of existing products
3. Retail Summarize sales across stores and determine busiest times to get staffing right
4. Data Science and Machine Learning Use aggregated data for training machine learning models or perform statistical analysis to identify trends in large datasets.
Benefits of aggregate data
Informed Decision-Making Aggregated data helps business people make data-driven decisions by offering a bird’s-eye view of trends across data sets.
Efficiency Simplifies analysis, saving time compared to processing individual data from raw files.
Better Visualization Enables clearer reporting through graphs, charts, and dashboards
Real-Time Insights Aggregating data in real-time allows for quick adaptation to market changes or operational needs.
Types of data aggregation
Temporal aggregation: Summarizing data over time (e.g., daily to monthly sales). Spatial aggregation: Combining data from specific geographic regions. Categorical aggregation: Grouping by categories, such as product type or customer demographics.
Understand the past, operate better today, and plan well for the future